
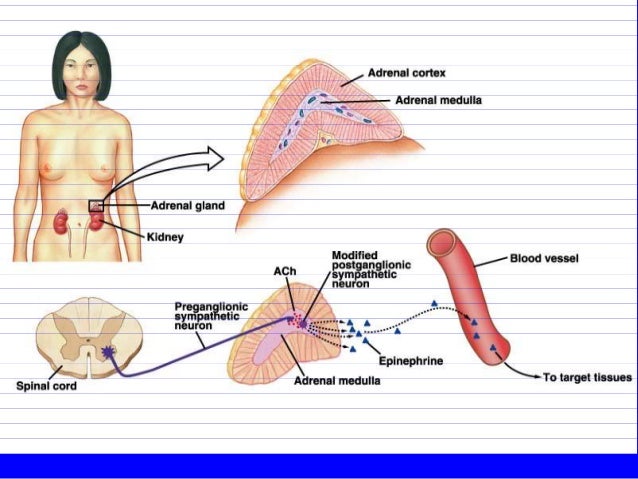
The right suprarenal vein drains into the inferior vena cava.

Venous drainage of the adrenal glands is achieved via the suprarenal veins: The inferior suprarenal artery is provided by the renal artery.The middle suprarenal artery is provided by the abdominal aorta.The superior suprarenal artery is provided by the inferior phrenic.
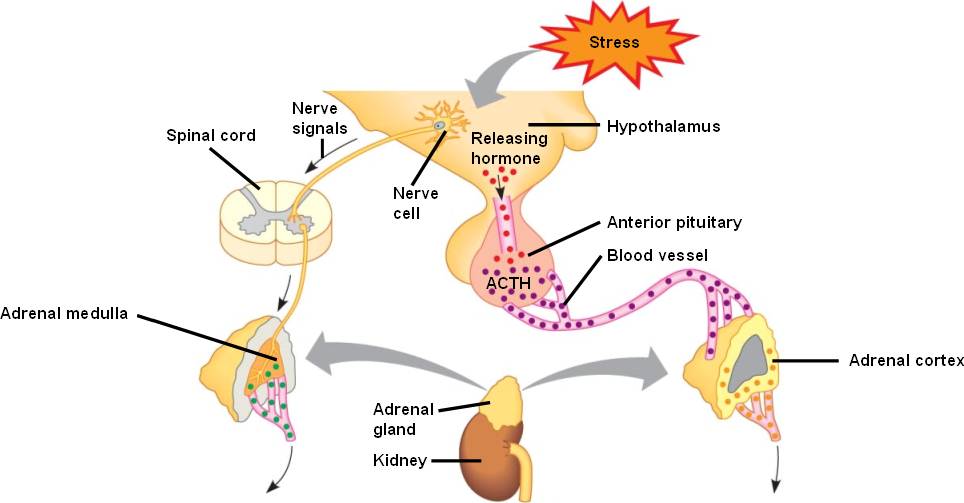
In contrast to the direct innervation of the medulla, the cortex is regulated by neuroendocrine hormones secreted by the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, as well as by the renin-angiotensin system.Īlthough variations of the blood supply to the adrenal glands (and indeed the kidneys themselves) are common, there are usually three arteries that supply each adrenal gland: Other cortical cells produce androgens such as testosterone, while some regulate water and electrolyte concentrations by secreting aldosterone. Some cells belong to the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and are the source of cortisol synthesis. Adrenal cortex By contrast, the adrenal cortex is devoted to the synthesis of corticosteroid hormones from cholesterol.It is also the main source of dopamine, a catecholamine closely related to adrenaline and noradrenaline.

The adrenal medulla can be considered specialized ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system, lacking distinct synapses, instead releasing secretions directly into the blood. These water-soluble hormones, derived from the amino acid tyrosine, are part of the fight-or-flight response initiated by the sympathetic nervous system. The chromaffin cells of the medulla are the body's main source of the catecholamine hormones adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
